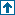



B = vb_sarvas_new(P, Q, R, S)
Magnetic field for multiple dipoles at a single MEG sensor
in spherical brain model (Sarvas Eq.)
INPUT
Dipole current source
P : current dipole position ( NP x 3 )
Q : current dipole moment ( NP x 3 )
MEG sensor
R : one of sensor position ( 1 x 3 ) or ( 3 x 1 )
S : its sensor orientation ( 1 x 3 ) or ( 3 x 1 )
OUTPUT
B : Lead field matrix ( NP x 1 )
Copyright (C) 2011, ATR All Rights Reserved.
License : New BSD License(see VBMEG_LICENSE.txt)

0001 function B = vb_sarvas_new(P, Q, R, S) 0002 % B = vb_sarvas_new(P, Q, R, S) 0003 % Magnetic field for multiple dipoles at a single MEG sensor 0004 % in spherical brain model (Sarvas Eq.) 0005 % 0006 % INPUT 0007 % Dipole current source 0008 % P : current dipole position ( NP x 3 ) 0009 % Q : current dipole moment ( NP x 3 ) 0010 % MEG sensor 0011 % R : one of sensor position ( 1 x 3 ) or ( 3 x 1 ) 0012 % S : its sensor orientation ( 1 x 3 ) or ( 3 x 1 ) 0013 % OUTPUT 0014 % B : Lead field matrix ( NP x 1 ) 0015 % 0016 % Copyright (C) 2011, ATR All Rights Reserved. 0017 % License : New BSD License(see VBMEG_LICENSE.txt) 0018 0019 % NP : # of dipole points 0020 % 0021 % 2004-12-15 Made by M. Sato 0022 0023 % Dipole position vector 0024 P1 = P(:,1); 0025 P2 = P(:,2); 0026 P3 = P(:,3); 0027 0028 % Dipole moment vector 0029 Q1 = Q(:,1); 0030 Q2 = Q(:,2); 0031 Q3 = Q(:,3); 0032 0033 % Sensor position vector 0034 R = R(:); 0035 R1 = R(1); 0036 R2 = R(2); 0037 R3 = R(3); 0038 0039 % Sensor orientation vector 0040 S = S(:); 0041 0042 % Difference from dipole to sensor : (NP x 3) 0043 dP = [(R1-P1), (R2-P2), (R3-P3)]; 0044 0045 % Square norm : (NP x 1) 0046 dd = sum(dP.^2, 2); 0047 d = sqrt(dd); 0048 rr = sum(R.^2); 0049 r = sqrt(rr); 0050 0051 % Inner product : (NP x 3) * ( 3 x 1 ) = (NP x 1) 0052 dr = dP*R; 0053 pr = P*R; 0054 0055 % Cross product (Q x P) : (NP x 3) 0056 QP = [Q2.*P3-Q3.*P2, ... 0057 Q3.*P1-Q1.*P3, ... 0058 Q1.*P2-Q2.*P1 ]; 0059 0060 % Denominator of magnetic potencial 0061 f = dd .* r + d .* dr ; 0062 0063 % ( Gradient of 'f' ) * S 0064 df = (d + dd./r).* (R'*S) + ( d + 2*r + dr./d ).* (dP*S); 0065 0066 % Magnetic field for sensor orientation vector 'S' 0067 B = (QP*S)./f - (QP*R).*df./(f.^2); 0068 B = (10^-7) * B; 0069 0070 return 0071 % END of program 0072 0073 %% Execution speed comparison with repmat 0074 % Time 0075 % 0.23 dP = [(R1-P1), (R2-P2), (R3-P3)]; 0076 % 0077 %% This code is faster than the following repmat code for large data 0078 %% since no memory allocation is needed 0079 % ( R1, R2, R3 are scalars) 0080 % 0081 % 0.36 R = repmat(R',[size(P,1) 1]); 0082 % 0.17 dP = R - P;